Go运行时network poller实现
network poller 是个啥?
先从实现一个telnet程序开始,回顾一下unix下的五种IO模型.
实现telnet
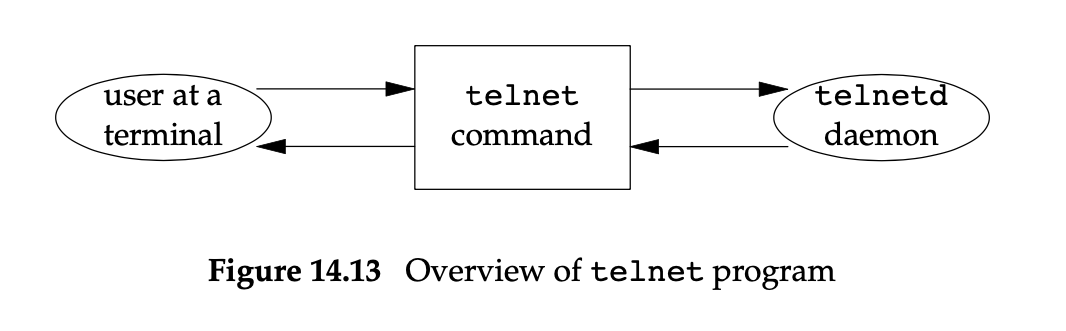
telnet命令 从终端读取命令写入网络连接,再从网络连接读取执行结果写回终端. 远端的telnetd程序读取输入的命令,在shell中进行执行,把执行命令产生的输出结果返回给用户.
blocking
如果我们只需要处理一个文件描述符, 一个循环搞定.
while ((n = read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, BUFSIZ)) > 0)
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n) != n)
err_sys("write error");
但是我们的telnet程序需要同时处理两个文件描述符, 怎么办?
并发方案开始登场啦
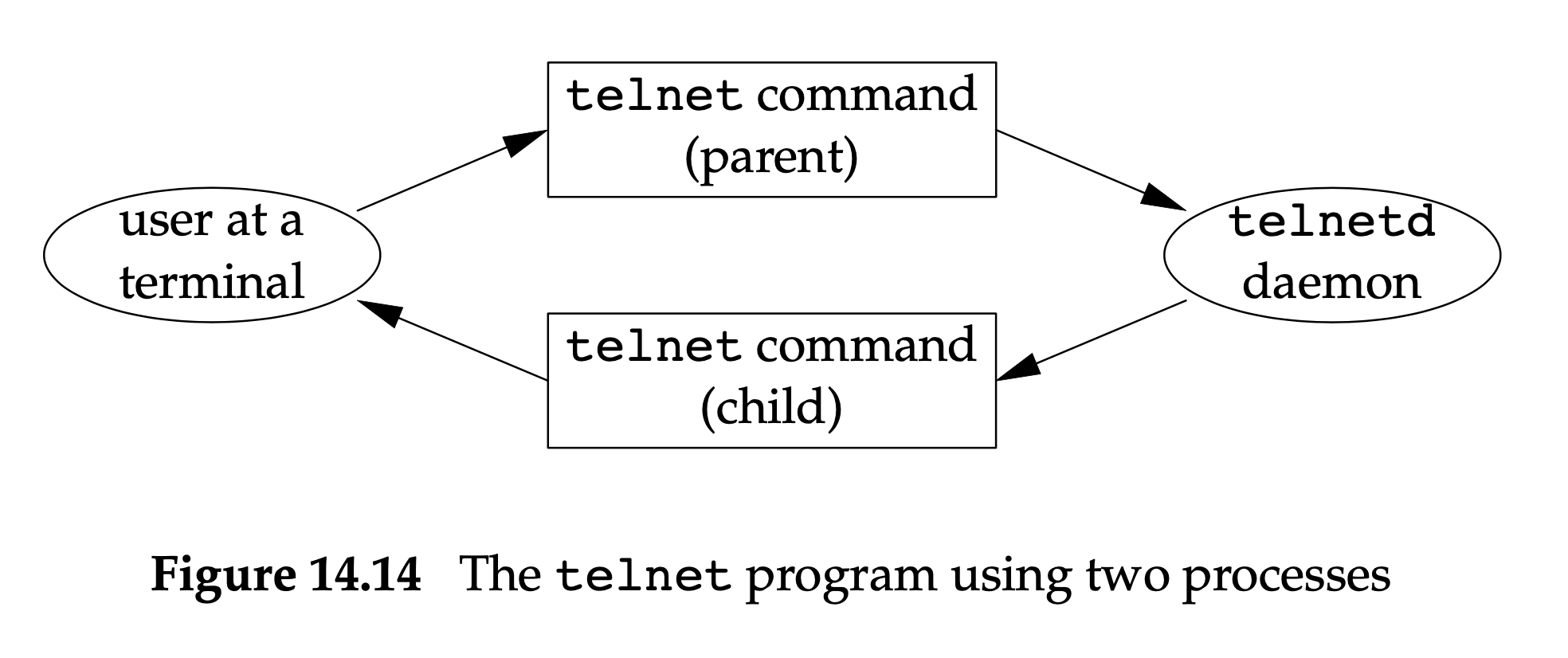
父子进程, 父进程负责从终端读取然后写入网络连接, 子进程负责从网络连接读取让后写入终端. 还需要处理两个父子进程之间的通信. 还可以在一个进程中使用两个线程, 但是需要处理两个线程数据的同步问题.
nonblocking
使用非阻塞的方案, 把两个文件描述符都设置成非阻塞的.
for (;;) {
if 尝试从stdin读取命令; 读到数据 {
处理数据写入,网络连接
} else if 出错 {
} else {
// EWOULDBLOCK 暂时没数据
}
if 尝试从网络连接读取; 读到数据 {
处理数据写入stdout
} else if 出错 {
} else {
// EWOULDBLOCK 暂时没数据
}
sleep 一会儿
}
This type of loop is called polling.
这种方法的缺点, sleep 时间太小浪费cpu,sleep时间太长不够及时.
I/O multiplexing
一种更好的方案, IO多路复用. 我们把所有自己关心的文件描述符放在一起,然后调用某个函数, 当有一个或者一批文件描述可以写或者读数据了, 调用返回, 通知程序哪些文件描述符可写或者可读.
fds = {terminalfd, netconn}
for (;;) {
readyfds = system_call(fds)
// 遍历可以处理的文件描述符进行处理
for fd = range readyfds {
// do something
}
}
IO多路复用的实现有很多, unix系统都支持(好像是) select/pselect/poll. 各个分支系统都有自己更高性能的方法. 比如 Linux epoll, BSD系包括macos kqueue, Solaris event port.
I/O 模型对比
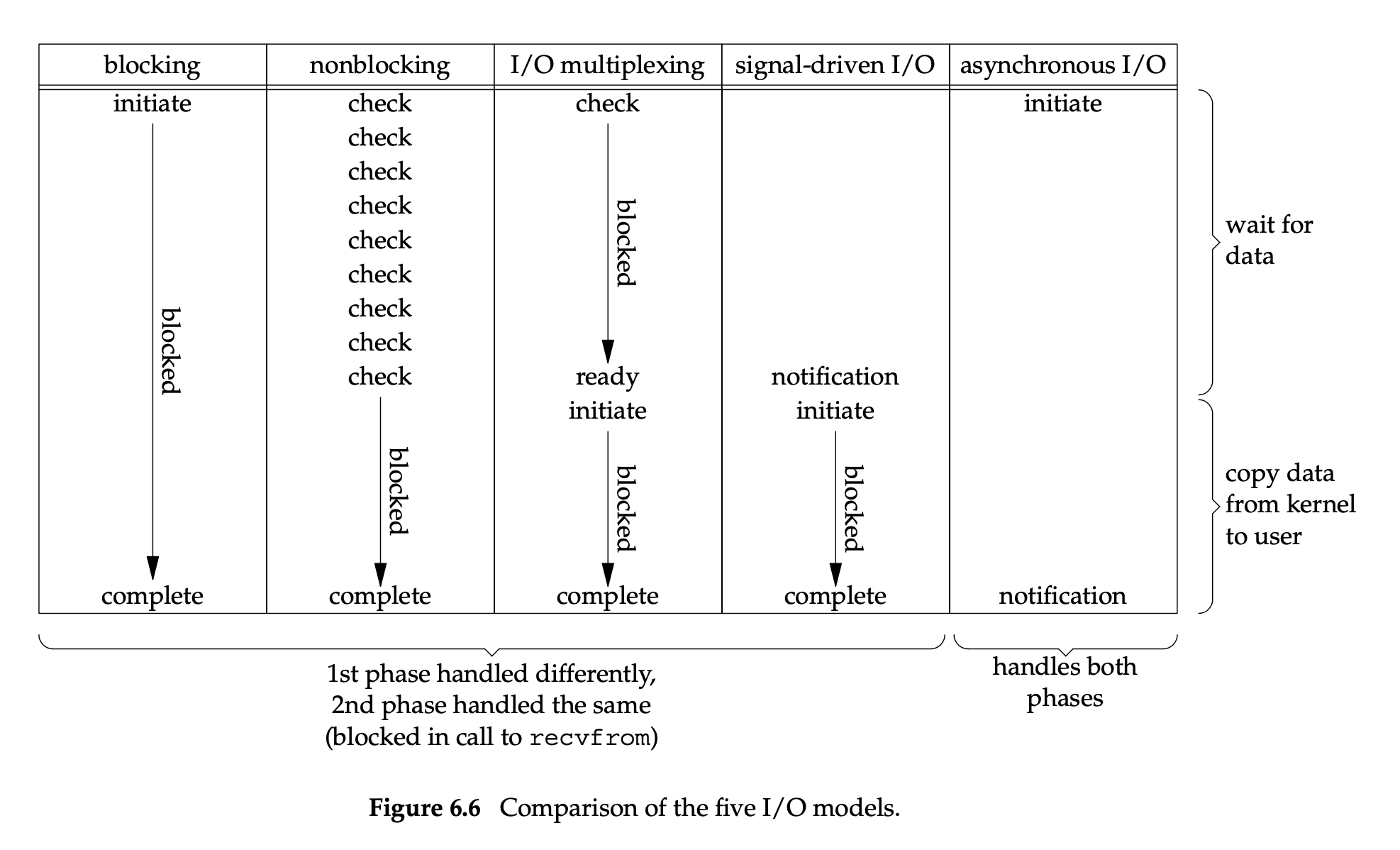
telnet到底用的啥?
每种系统的实现不太一样
linux
/*
* Check to see if any out-of-band data exists on a socket (for
* Telnet "synch" processing).
*/
int
stilloob (void)
{
static struct timeval timeout = { 0, 0 };
fd_set excepts;
int value;
do
{
FD_ZERO (&excepts);
FD_SET (net, &excepts);
value =
select (net + 1, (fd_set *) 0, (fd_set *) 0, &excepts, &timeout);
}
while ((value == -1) && (errno == EINTR));
if (value < 0)
{
perror ("select");
(void) quit ();
}
if (FD_ISSET (net, &excepts))
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
freebsd
/*
* Check to see if any out-of-band data exists on a socket (for
* Telnet "synch" processing).
*/
int
stilloob(void)
{
struct pollfd pfd[1];
int value;
do {
pfd[0].fd = net;
pfd[0].events = POLLRDBAND;
value = poll(pfd, 1, 0);
} while ((value == -1) && (errno == EINTR));
if (value < 0) {
perror("poll");
quit();
}
if (pfd[0].revents & POLLRDBAND)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
go运行时中的network poller
go运行时中的network poller是对各种操作系统中的IO多路复用实现的统一封装. 根据不同的系统环境选择最优的实现.
runtime network poller 实现
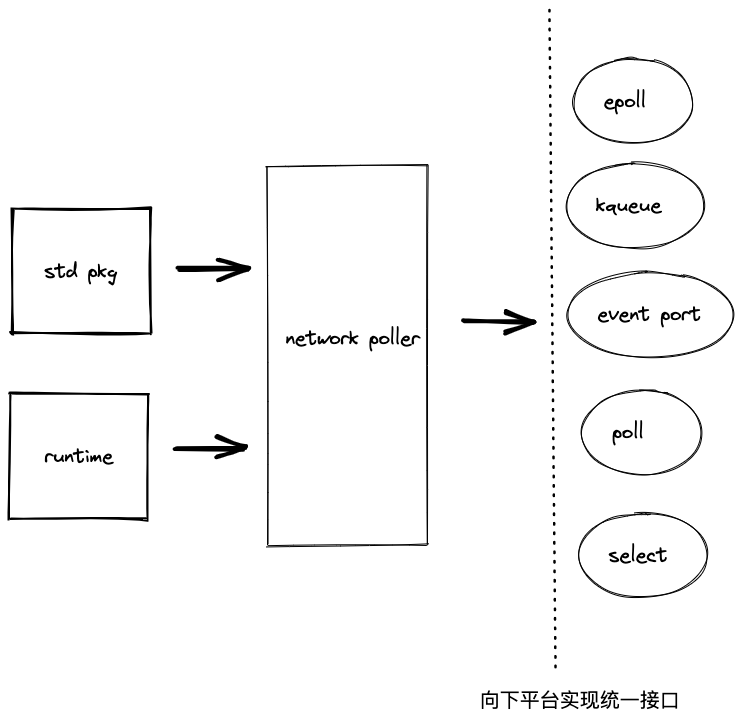
network poller 向下对各种平台相关IO多路复用方法进行统一封装. 向上为标准库和运行时提供方法使用network poller.
- 统一定义的平台无关多路复用接口,各种实现都需要定义以下方法.
// Integrated network poller (platform-independent part).
// A particular implementation (epoll/kqueue/port/AIX/Windows)
// must define the following functions:
//
// func netpollinit()
// Initialize the poller. Only called once.
//
// func netpollopen(fd uintptr, pd *pollDesc) int32
// Arm edge-triggered notifications for fd. The pd argument is to pass
// back to netpollready when fd is ready. Return an errno value.
//
// func netpollclose(fd uintptr) int32
// Disable notifications for fd. Return an errno value.
//
// func netpoll(delta int64) gList
// Poll the network. If delta < 0, block indefinitely. If delta == 0,
// poll without blocking. If delta > 0, block for up to delta nanoseconds.
// Return a list of goroutines built by calling netpollready.
//
// func netpollBreak()
// Wake up the network poller, assumed to be blocked in netpoll.
//
// func netpollIsPollDescriptor(fd uintptr) bool
// Reports whether fd is a file descriptor used by the poller.
- 提供给标准库使用相关的方法
func runtime_pollServerInit()
func runtime_pollOpen(fd uintptr) (uintptr, int)
func runtime_pollClose(ctx uintptr)
func runtime_pollWait(ctx uintptr, mode int) int
func runtime_pollWaitCanceled(ctx uintptr, mode int) int
func runtime_pollReset(ctx uintptr, mode int) int
func runtime_pollSetDeadline(ctx uintptr, d int64, mode int)
func runtime_pollUnblock(ctx uintptr)
func runtime_isPollServerDescriptor(fd uintptr) bool
- 提供给runtime使用的相关方法
func netpoll(delta int64) gList
func netpollBreak()
下面是相关主要方法在mac上使用kqueue的具体实现.
Network poller descriptor
type pollDesc struct {
link *pollDesc // in pollcache, protected by pollcache.lock
// The lock protects pollOpen, pollSetDeadline, pollUnblock and deadlineimpl operations.
// This fully covers seq, rt and wt variables. fd is constant throughout the PollDesc lifetime.
// pollReset, pollWait, pollWaitCanceled and runtime·netpollready (IO readiness notification)
// proceed w/o taking the lock. So closing, everr, rg, rd, wg and wd are manipulated
// in a lock-free way by all operations.
// NOTE(dvyukov): the following code uses uintptr to store *g (rg/wg),
// that will blow up when GC starts moving objects.
lock mutex // protects the following fields
fd uintptr
closing bool
everr bool // marks event scanning error happened
user uint32 // user settable cookie
rseq uintptr // protects from stale read timers
rg uintptr // pdReady, pdWait, G waiting for read or nil
rt timer // read deadline timer (set if rt.f != nil)
rd int64 // read deadline
wseq uintptr // protects from stale write timers
wg uintptr // pdReady, pdWait, G waiting for write or nil
wt timer // write deadline timer
wd int64 // write deadline
self *pollDesc // storage for indirect interface. See (*pollDesc).makeArg.
}
文件描述符在netpoller中的封装, 增加状态/定时器的相关附加字段.
Networker poller 初始化
//go:linkname poll_runtime_pollServerInit internal/poll.runtime_pollServerInit
func poll_runtime_pollServerInit() {
netpollGenericInit()
}
func netpollGenericInit() {
// ...
netpollinit()
// ...
}
func netpollinit() {
kq = kqueue()
if kq < 0 {
println("runtime: kqueue failed with", -kq)
throw("runtime: netpollinit failed")
}
closeonexec(kq)
r, w, errno := nonblockingPipe()
if errno != 0 {
println("runtime: pipe failed with", -errno)
throw("runtime: pipe failed")
}
ev := keventt{
filter: _EVFILT_READ,
flags: _EV_ADD,
}
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&ev.ident)) = uintptr(r)
n := kevent(kq, &ev, 1, nil, 0, nil)
if n < 0 {
println("runtime: kevent failed with", -n)
throw("runtime: kevent failed")
}
netpollBreakRd = uintptr(r)
netpollBreakWr = uintptr(w)
}
- 初始化kqueue. (linux 是epoll)
- 使用pipe创建一对读写文件句柄, 并把获得的句柄加入kqueue中监听, 用于主动结束 netpoll等待
runtime_pollOpen 新增句柄
//go:linkname poll_runtime_pollOpen internal/poll.runtime_pollOpen
func poll_runtime_pollOpen(fd uintptr) (*pollDesc, int) {
pd := pollcache.alloc()
// ... reset pd
errno := netpollopen(fd, pd)
if errno != 0 {
pollcache.free(pd)
return nil, int(errno)
}
return pd, 0
}
func netpollopen(fd uintptr, pd *pollDesc) int32 {
// Arm both EVFILT_READ and EVFILT_WRITE in edge-triggered mode (EV_CLEAR)
// for the whole fd lifetime. The notifications are automatically unregistered
// when fd is closed.
var ev [2]keventt
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&ev[0].ident)) = fd
ev[0].filter = _EVFILT_READ
ev[0].flags = _EV_ADD | _EV_CLEAR
ev[0].fflags = 0
ev[0].data = 0
ev[0].udata = (*byte)(unsafe.Pointer(pd))
ev[1] = ev[0]
ev[1].filter = _EVFILT_WRITE
n := kevent(kq, &ev[0], 2, nil, 0, nil)
if n < 0 {
return -n
}
return 0
}
将传入的句柄加入network poller的处理中.
netpoll 运行时检查获取ready的句柄
// netpoll checks for ready network connections.
// Returns list of goroutines that become runnable.
// delay < 0: blocks indefinitely
// delay == 0: does not block, just polls
// delay > 0: block for up to that many nanoseconds
func netpoll(delay int64) gList {
// ....
var events [64]keventt
retry:
n := kevent(kq, nil, 0, &events[0], int32(len(events)), tp)
if n < 0 {
// ...
}
var toRun gList
for i := 0; i < int(n); i++ {
ev := &events[i]
if uintptr(ev.ident) == netpollBreakRd {
// ...
}
var mode int32
switch ev.filter {
case _EVFILT_READ:
mode += 'r'
if ev.flags&_EV_EOF != 0 {
mode += 'w'
}
case _EVFILT_WRITE:
mode += 'w'
}
if mode != 0 {
pd := (*pollDesc)(unsafe.Pointer(ev.udata))
pd.everr = false
if ev.flags == _EV_ERROR {
pd.everr = true
}
netpollready(&toRun, pd, mode)
}
}
return toRun
}
func netpollready(toRun *gList, pd *pollDesc, mode int32) {
var rg, wg *g
if mode == 'r' || mode == 'r'+'w' {
rg = netpollunblock(pd, 'r', true)
}
if mode == 'w' || mode == 'r'+'w' {
wg = netpollunblock(pd, 'w', true)
}
if rg != nil {
toRun.push(rg)
}
if wg != nil {
toRun.push(wg)
}
}
func netpollunblock(pd *pollDesc, mode int32, ioready bool) *g {
gpp := &pd.rg
if mode == 'w' {
gpp = &pd.wg
}
for {
old := *gpp
if old == pdReady {
return nil
}
if old == 0 && !ioready {
// Only set pdReady for ioready. runtime_pollWait
// will check for timeout/cancel before waiting.
return nil
}
var new uintptr
if ioready {
new = pdReady
}
if atomic.Casuintptr(gpp, old, new) {
if old == pdWait {
old = 0
}
return (*g)(unsafe.Pointer(old))
}
}
}
runtime_pollWait goroutine等待某个句柄ready
// poll_runtime_pollWait, which is internal/poll.runtime_pollWait,
// waits for a descriptor to be ready for reading or writing,
// according to mode, which is 'r' or 'w'.
// This returns an error code; the codes are defined above.
//go:linkname poll_runtime_pollWait internal/poll.runtime_pollWait
func poll_runtime_pollWait(pd *pollDesc, mode int) int {
for !netpollblock(pd, int32(mode), false) {
}
return pollNoError
}
// returns true if IO is ready, or false if timedout or closed
// waitio - wait only for completed IO, ignore errors
func netpollblock(pd *pollDesc, mode int32, waitio bool) bool {
gpp := &pd.rg
if mode == 'w' {
gpp = &pd.wg
}
// set the gpp semaphore to pdWait
for {
old := *gpp
if old == pdReady {
*gpp = 0
return true
}
if old != 0 {
throw("runtime: double wait")
}
if atomic.Casuintptr(gpp, 0, pdWait) {
break
}
}
// need to recheck error states after setting gpp to pdWait
// this is necessary because runtime_pollUnblock/runtime_pollSetDeadline/deadlineimpl
// do the opposite: store to closing/rd/wd, membarrier, load of rg/wg
if waitio || netpollcheckerr(pd, mode) == 0 {
gopark(netpollblockcommit, unsafe.Pointer(gpp), waitReasonIOWait, traceEvGoBlockNet, 5)
}
// be careful to not lose concurrent pdReady notification
old := atomic.Xchguintptr(gpp, 0)
if old > pdWait {
throw("runtime: corrupted polldesc")
}
return old == pdReady
}
检查句柄是否ready, 如果没有, gopark.
runtime_pollSetDeadline 设置等待超时时间
//go:linkname poll_runtime_pollSetDeadline internal/poll.runtime_pollSetDeadline
func poll_runtime_pollSetDeadline(pd *pollDesc, d int64, mode int) {
// ...
rd0, wd0 := pd.rd, pd.wd
combo0 := rd0 > 0 && rd0 == wd0
if d > 0 {
d += nanotime()
if d <= 0 {
// If the user has a deadline in the future, but the delay calculation
// overflows, then set the deadline to the maximum possible value.
d = 1<<63 - 1
}
}
if mode == 'r' || mode == 'r'+'w' {
pd.rd = d
}
if mode == 'w' || mode == 'r'+'w' {
pd.wd = d
}
combo := pd.rd > 0 && pd.rd == pd.wd
rtf := netpollReadDeadline
if combo {
rtf = netpollDeadline
}
if pd.rt.f == nil {
if pd.rd > 0 {
pd.rt.f = rtf
// Copy current seq into the timer arg.
// Timer func will check the seq against current descriptor seq,
// if they differ the descriptor was reused or timers were reset.
pd.rt.arg = pd.makeArg()
pd.rt.seq = pd.rseq
resettimer(&pd.rt, pd.rd)
}
} else if pd.rd != rd0 || combo != combo0 {
pd.rseq++ // invalidate current timers
if pd.rd > 0 {
modtimer(&pd.rt, pd.rd, 0, rtf, pd.makeArg(), pd.rseq)
} else {
deltimer(&pd.rt)
pd.rt.f = nil
}
}
if pd.wt.f == nil {
if pd.wd > 0 && !combo {
pd.wt.f = netpollWriteDeadline
pd.wt.arg = pd.makeArg()
pd.wt.seq = pd.wseq
resettimer(&pd.wt, pd.wd)
}
}
// ...
}
func netpolldeadlineimpl(pd *pollDesc, seq uintptr, read, write bool) {
// ...
rg = netpollunblock(pd, 'r', false)
// ...
wg = netpollunblock(pd, 'w', false)
if rg != nil {
netpollgoready(rg, 0)
}
if wg != nil {
netpollgoready(wg, 0)
}
}
runtime_pollUnblock 取消等待, 让对应的goroutine ready
//go:linkname poll_runtime_pollUnblock internal/poll.runtime_pollUnblock
func poll_runtime_pollUnblock(pd *pollDesc) {
lock(&pd.lock)
if pd.closing {
throw("runtime: unblock on closing polldesc")
}
pd.closing = true
pd.rseq++
pd.wseq++
var rg, wg *g
atomic.StorepNoWB(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&rg)), nil) // full memory barrier between store to closing and read of rg/wg in netpollunblock
rg = netpollunblock(pd, 'r', false)
wg = netpollunblock(pd, 'w', false)
if pd.rt.f != nil {
deltimer(&pd.rt)
pd.rt.f = nil
}
if pd.wt.f != nil {
deltimer(&pd.wt)
pd.wt.f = nil
}
unlock(&pd.lock)
if rg != nil {
netpollgoready(rg, 3)
}
if wg != nil {
netpollgoready(wg, 3)
}
}
自顶向下-从一个TCP server的视角看network poller
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net"
"time"
)
func main() {
l, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8080")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
for {
conn, err := l.Accept()
if err != nil {
}
go serve(conn)
}
}
func serve(conn net.Conn) {
for {
data := make([]byte, 1024)
conn.SetDeadline(time.Now().Add(5 * time.Second))
n, err := conn.Read(data)
if err != nil {
// check timeout
if err, ok := err.(net.Error); ok && err.Timeout() {
fmt.Println("timeout")
continue
}
return
}
fmt.Printf("read %d byte data from %v\n", n, conn.RemoteAddr())
}
}
- 程序监听:8080端口, net.Listen 会调用socket从os获得一个fd, 并把这个fd调用 poll_runtime_pollOpen internal/poll.runtime_pollOpen 注册进 network poller.
- l.Accept(). main goroutine会